If you own an AMD Ryzen CPU and have done a Google search for information about RAM overclocking, speed, and stability in the last 7 years, chances are you might have come across something called the “Infinity Fabric.” Usually brought into discussions to explain the somewhat unique relationship of AMD CPUs with high-speed memory, Infinity Fabric is an internal interconnect bus that forms the core of AMD’s scalable CPU architecture.
It not only links the various components of AMD’s CPU chiplets to each other, but also acts as a chiplet-chiplet, CPU-CPU, and CPU-GPU interconnect, acting as a flexible and scalable solution for high-speed data transfer. AMD’s multi-chip module (MCM) design relies heavily on Infinity Fabric to make sense of the economics of engineering CPU dies.
Related
Ready to switch from Intel? Here are the 6 best AMD CPU upgrades
If you’re building or upgrading a PC and are ready to make the jump to Ryzen, these are the best AMD CPUs for your rig.
What exactly is AMD’s Infinity Fabric?
To infinity and beyond
Source: AMD
Prior to the launch of AMD’s Zen architecture in 2017, the company used HyperTransport, an interconnect technology linking multiple CPUs and I/O devices together in multi-processor systems. AMD evolved HyperTransport into Infinity Fabric to enable efficient multi-die connection and scalability when creating its “Zen” architecture for the EPYC and Ryzen CPUs.
So, Infinity Fabric became AMD’s new interconnect technology to power its shift from monolithic CPU tiles into a chiplet-based design. It is now at the heart of AMD’s Ryzen CPUs, connecting multiple CPU cores, chiplets, caches and memory controllers, and integrated GPUs in a scalable structure.
AMD also uses Infinity Fabric for its socket-to-socket CPU interconnect and between data center GPUs in server environments. The company successfully modified its previous HyperTransport technology to create a homogenous data interconnect protocol across its commercial and consumer products, aiding innovation and powering its decentralized CPU architecture.

Related
AMD’s Zen architecture: The fundamentals of these Zen 4 CPUs
Zen transformed AMD from a company on the verge of bankruptcy into a leader of the computing industry with Zen 4. Here’s everything you need to know.
Why did AMD need to develop Infinity Fabric?
The need of the hour
Source: AMD
I touched upon this briefly in the previous section, but it demands its own segment here, owing to the fact that AMD realized immense benefits from its move to Infinity Fabric. For starters, AMD’s modular chiplet design wouldn’t work as intended without a high-speed data interconnect. Thanks to Infinity Fabric, AMD could move away from monolithic dies that can be costly to develop, and also decouple various components of a CPU die from each other, enabling better and consistent gen-on-gen improvements.
Besides improving yields by manufacturing smaller dies plus the scalability benefits, Infinity Fabric also allowed AMD to unify its interconnect technologies across its multiple product lines and markets. This streamlined innovation and development, which enabled the company to cross-leverage its successes from the data center market into the consumer market.
Next, Infinity Fabric provided much higher bandwidth and lower latency compared to AMD’s previous interconnect technology, allowing the CPU to efficiently adjust clock speeds as well as memory performance for the best results. AMD first engineered Infinity Fabric for use in its EPYC server line of CPUs and later implemented it on its consumer CPUs.

Related
How does Infinity Fabric work on your Ryzen CPU?
How does it matter to the average consumer?
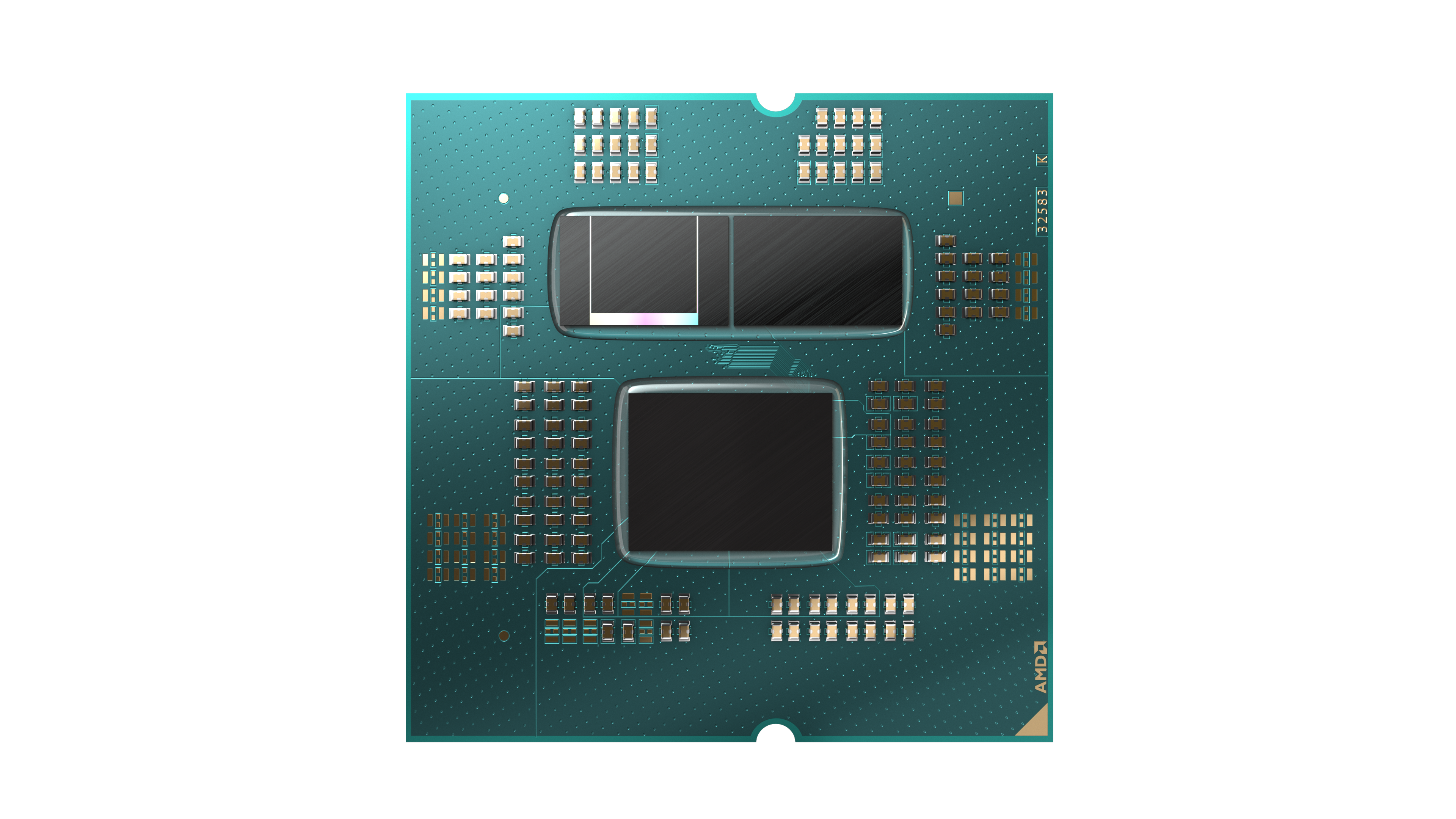
As I mentioned, Infinity Fabric acts as the data highway connecting individual components of a Ryzen processor. On a single Core Complex (CCX) — essentially a cluster of up to 4 cores, and L1 and L2 caches — Infinity Fabric ensures fast communication between the cores and caches. On the Core Complex Die (CCD) level, a CCD can contain one or two CCXs. Infinity Fabric connects the CCXs, memory controller, and the shared L3 cache together.
On Ryzen CPUs that have multiple CCDs (currently only on Ryzen 9 processors), Infinity Fabric connects the cores on different CCDs together and the CCDs with the I/O die. It also ensures efficient data transfer between the dies and external components like memory and peripherals. Finally, Infinity Fabric runs in sync with the memory frequency for minimal latency.
Fun fact — Infinity Fabric has its own frequency known as FCLK, which runs in a 1:1 configuration with the memory clock or MCLK. So, if your RAM kit is rated for 6,000MT/s, its MCLK will be half of 6,000 i.e 3,000MT/s, and this is what the Infinity Fabric will also operate at, to maintain the 1:1 configuration and optimum performance. Although you can manually enable a 2:1 FCLK:MCLK ratio to run faster memory, it will introduce additional latency.

Related
4 reasons why RAM timings matter
RAM isn’t just segmented into DDR versions or mega transfers. Timings matter too.